Surgery Center
With a board certified equine surgeon and a full service surgery center, Chicago Equine is equipped to provide a wide range of procedures including emergency and elective surgeries. Post operatively, an experienced team is available around the clock to provide the care and attention our surgery patients require.
Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is an advanced minimally invasive technique for performing joint surgery in the horse. Arthroscopy is performed for a variety of reasons including the treatment of OCD, chip removal, and select fracture repairs involving joints. Additionally, injuries to the soft tissues and ligaments inside joints may be diagnosed and treated using this technique. Advanced regenerative modalities such as stem cell therapy can also be precisely delivered to the site of injury under direct visualization.
The procedure involves the insertion of a small rigid camera into the joint through a small (3/4”) incision over the joint capsule under general anesthesia. Specialized small instruments are then passed through a second small incision to treat your horse’s specific problem. The incisions are closed with two or three small sutures. Some of the many benefits of arthroscopy include less tissue trauma, decreased risk of infection, an earlier return to activity, a shortened hospital stay, and precise application of therapeutic agents to injured tissue.
Colic Surgery
Colic in the horse is defined as abdominal pain and should always be considered an emergency. Commonly this is due to some disturbance of the intestines; though any organ in the abdomen may cause colic in the horse. Fortunately the vast majority of colic episodes in horses resolve with minimal medical therapy in our hospital. In the small percentage of horses that do not respond quickly and completely with medical therapy, surgery may be indicated. The decision to recommend surgery for your horse is based upon many complex factors including level and duration of pain, cardiovascular status, blood work results, abdominal fluid analysis, ultrasound findings, and changes in vital parameters (pulse, respiration, etc). We will communicate with you every step of the way to help you make the very best informed decision for your horse.
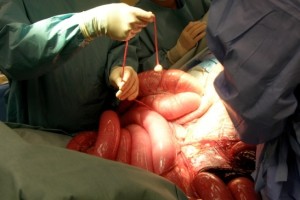 Once the decision has been made to proceed with surgery, the horse is placed under general anesthesia. The surgery is performed through a midline incision near the horse’s umbilicus. Following correction of the issue, the abdominal wall is closed in three layers and the horse is carefully placed in a padded recovery stall. Recovery from anesthesia is critically monitored and the horse is assisted to stand when ready. In general, horses will stay in the hospital for approximately 5-7 days following surgery and then be discharged under the close supervision of your horse’s primary veterinarian. Approximately 3 months after colic surgery horses may return to their previous work.
Once the decision has been made to proceed with surgery, the horse is placed under general anesthesia. The surgery is performed through a midline incision near the horse’s umbilicus. Following correction of the issue, the abdominal wall is closed in three layers and the horse is carefully placed in a padded recovery stall. Recovery from anesthesia is critically monitored and the horse is assisted to stand when ready. In general, horses will stay in the hospital for approximately 5-7 days following surgery and then be discharged under the close supervision of your horse’s primary veterinarian. Approximately 3 months after colic surgery horses may return to their previous work.
The prognosis for horses undergoing colic surgery is directly related to which portion of the intestinal system is affected, the severity and duration of the problem, and the amount of cardiovascular compromise. Thanks to advances in surgical techniques and post-operative care therapies, the general prognosis for most horses undergoing colic surgery is good and constantly improving.
Orthopedic Conditions
Orthopedic conditions in the horse requiring surgery are quite varied and include bone fractures, osteochondrosis (OCD), joint fragments (chips), and angular limb deformities in foals (crooked legs). We commonly diagnose and treat these, among other orthopedic conditions, at our surgical center. Advanced surgical implants and techniques are provided to ensure your horse has the best outcome possible.
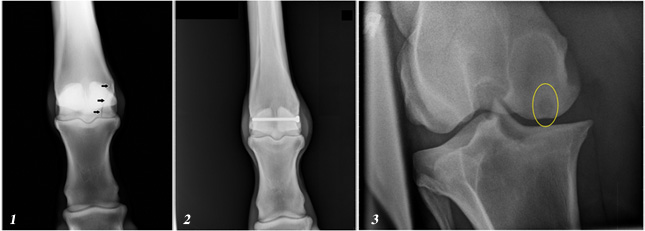
Above: Figure 1 – Condylar fracture sustained while racing; Figure 2 -The same fracture as in Fig.1a three months after surgery; Figure 3 – Cystic lesion in the stifle.
Upper Respiratory/Airway Surgery
Respiratory conditions affecting the upper airway of horses can be a significant cause of poor performance in the equine athlete. Through our use of video endoscopy and clinical experience we have the ability to accurately diagnose and treat these frustrating problems.
Laryngeal hemiplegia (“roarer”), displacement of the soft palate, chondritis, and entrapment of the epiglottis are just a few examples of issues that occur in the larynx region of the throat.
The paranasal sinuses of the horse are quite complex and are another area of the respiratory system of the horse that may develop conditions requiring surgery. Paranasal sinus cyst, neoplasia (cancer), and dental disease are examples of surgical conditions of the sinuses.
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive method of performing abdominal surgery by the use of a long rigid camera and specialized instruments. We can perform laparoscopy either under general anesthesia or, in select cases, while the horse is sedated and standing. This advanced technique of surgery allows for decreased lay-up time, less discomfort, and direct visualization of the standing horse’s abdomen.
The most common reason to perform laparoscopy in the male is for removal of cryptorchid testicles. In the female, ovarian issues necessitating the removal of one or both ovaries is commonly performed via standing laparoscopy.
In select cases of recurring colic, laparoscopic techniques have been developed to allow permanent prevention of a specific cause of colic.
Reproductive/Urogenital Surgery
The urinary and reproductive systems of the horse may also require surgery.
Bladder stones, castration (cryptorchids), bladder rupture, neoplasia (cancer) and ovarian tumors are some examples of conditions requiring surgery of the urogenital tract that we perform.
Mares may also damage their caudal reproductive tract during foaling and require reconstructive surgery.
Wound Reconstruction
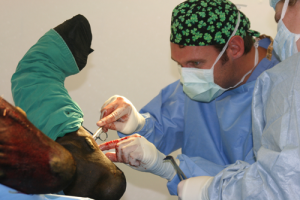 While most simple wounds respond well to treatment on the farm, some wounds require intensive treatment at our surgical center. Extensive lacerations, tendon lacerations, and wounds involving joints are better served by surgical repair. We are experienced with advanced therapy such as skin grafting as well, should your horse require it.
While most simple wounds respond well to treatment on the farm, some wounds require intensive treatment at our surgical center. Extensive lacerations, tendon lacerations, and wounds involving joints are better served by surgical repair. We are experienced with advanced therapy such as skin grafting as well, should your horse require it.














